Galaxy S22 developer options let you access some hidden or advanced or experimental features of your Galaxy S22, S22+ and S22 Ultra.
This Galaxy S22 how-to guide explains what Galaxy S22 developer options are, why and when you may need them, how to enable Galaxy S22 developer options, and finally, all entries of Galaxy S22 developer options are explained in simple language.
If your Galaxy S21, S20, or S10 has been updated to Android 12, Galaxy S22 developer options also apply to these phones. For Galaxy S22, S21, and S20 with Android 13 (One UI 5) update, you may find a few additional options, as explained here.
Android 14 (One UI 6) update has been rolled out to Galaxy S22 with many new features you should try.
Everything about enabling and using Galaxy S22 Developer Options
- What are Galaxy S22 Developer Options? Why and when you may need it?
- How to enable and access Galaxy S22 Developer Options
- Galaxy S22 developer options explained
- 1. On/off Galaxy S22 developer options
- 2. Memory
- 3. Bug report
- 4. Desktop backup password
- 5. Stay awake
- 6. Enable Bluetooth HCI snoop log
- 7. OEM unlocking
- 8. Running services
- 9. Picture colour mode
- 10. Webview implementation
- 11. Auto update system
- 12. Demo mode
- 13. Quik settings developer tiles
- 14. USB debugging
- 15. Revoke USB debugging authorizations
- 16. 3GPP AT commands
- 17. Wireless debugging
- 18. Disable adb authorization timeout
- 19. Bug report shortcut
- 20. Verbose vendor logging
- 21. Enable view attribute inspection
- 22. Select debug app
- 23. Wait for debugger
- 24. Verify apps over USB
- 25. Verify bytecode of debuggable apps
- 26. Logger buffer sizes
- 27. Samsung verbose debug logging
- 28. Feature flags
- 29. Enable GPU debug layers
- 30. Graphics driver
- 31. App compatibility change
- 32. Show refresh rate
- 33. Allow screen overlays on Settings
- 34. System Tracing
- 35. Wireless display certification
- 36. Enable Wi-Fi verbose logging
- 37. Wi-Fi safe mode
- 38. Wi-Fi scan throttling
- 39. Enhanced Wi-Fi MAC randomization
- 40. Mobile data always active
- 41. Tethering hardware acceleration
- 42. Default USB configuration
- 43. Show Bluetooth devices without names
- 44. Disable absolute volume
- 45. Turn off AVC block list
- 46. Turn off A2DP hardware offload
- 47. Bluetooth AVRCP version
- 48. HD audio
- 49. Bluetooth audio codec
- 50. Bluetooth Audio sample rate
- 51. Bluetooth audio bits per sample
- 52. Bluetooth audio channel mode
- 53. Bluetooth audio LDAC codec
- 54. Bluetooth PBAP
- 55. Show taps
- 56. Pointer location
- 57. Show surface updates
- 58. Show layout bounds
- 59. Force RTL layout direction
- 60. Windo animation scale
- 61. Transition animation scale
- 62. Animation duration scale
- 63. Simulate secondary displays
- 64. Minimum width
- 65. Simulate display cutout
- 66. Show Text ID
- 67. Show view updates
- 68. Show hardware layer update
- 69. Debug GPU overdraw
- 70. Debug non-rectangular clip operations
- 71. Force dark mode
- 72. Force 4x MSAA
- 73. Disable HW overlays
- 74. Simulate colour space
- 75. GPUWatch
- 76. Disable USB audio routing
- 77. Media transcoding settings
- 78. Strict mode enabled
- 79. Profile HWUI rendering
- 80. Don’t keep activities
- 81. Background process limit
- 82. Background check
- 83. Always show crash dialog
- 84. Show background ANRs
- 85. Suspend execution for cached apps
- 86. Show notification channel warnings and reset notification importance
- 87. Standby apps
- 88. Force allow apps on external
- 89. Force activities to be resizable
- 90. Enable freeform windows
- 91. Force desktop mode
- 92. Multi-window for all apps
- 93. Reset the ShortcutManager API call limit
- 94. Logging level
- 95. Max requests per session
- 96. Max visible datasets
- 97. Reset to default values
- 98. Shared data
- 99. Select mock location app
- 100. Force full GNSS
What are Galaxy S22 Developer Options? Why and when you may need it?
Like all other Android devices, Galaxy S22, S22+ and S22 Ultra also offer developer options.
In a nutshell, Galaxy S22 developer options are a collection of features that are not available in the user interface by default. These may include some deprecated, beta, experimental, and special features for developers and advanced users.
Galaxy S22 developer options are mainly for developers and Android enthusiasts. But the hidden features, experimental features, and a few advanced features can be useful for normal users.
For example, if you use Samsung DeX, you can use Galaxy S22 developer options to force all apps to be resizable and overwrite the manifest settings.
Many Galaxy S22 owners, especially developers, often use USB debugging to test apps, run ADB (Android Debug Bridge) commands, and check system processes. We also use ADB to take screenshots (when we need to take a lot of them).
Also, when you own high-end wireless headphones or earbuds, you may enjoy the audio with better quality by enabling the corresponding codec. For Galaxy Buds Pro or Galaxy Buds Pro 2 users, you may enjoy Hi-Fi level audio using Samsung Sealess Codec. For Sony WF-1000XM4/XM5 owners, you may even enjoy the Hi-Res Audio with the LDAC codec on Galaxy S22 and S23. But some of the settings can only be accessed through developer options.
However, if you are not sure whether you need to use Galaxy S22 developer options, you very likely do not need them.
The number one rule of using Galaxy S22 developer options is that you should enable/disable the feature that you know. Never touch the features you are not sure about.
How to enable and access Galaxy S22 Developer Options
By default, the developer options on Galaxy S22 are hidden.
You may follow these steps to enable Galaxy S22 developer options.
Step 1: Open Galaxy S22 Settings
There are a couple of different ways to open Galaxy S22 settings. For example,
- Tap the Settings app icon (gear icon) on the Galaxy S22 Home screen or Apps screen.
- Tap the Gear icon in the Galaxy S22 Quick Settings panel or notification panel.
- Use voice commands (Google Assistant or Bixby).
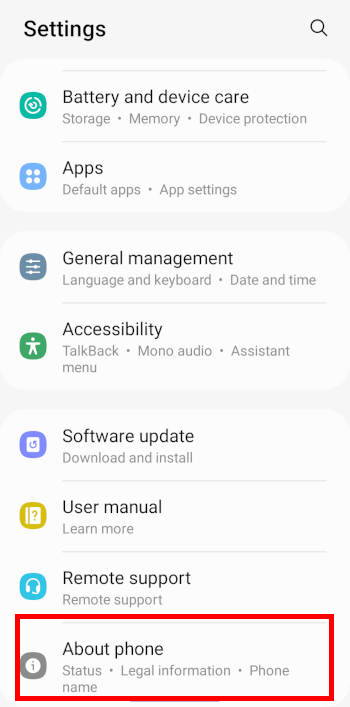
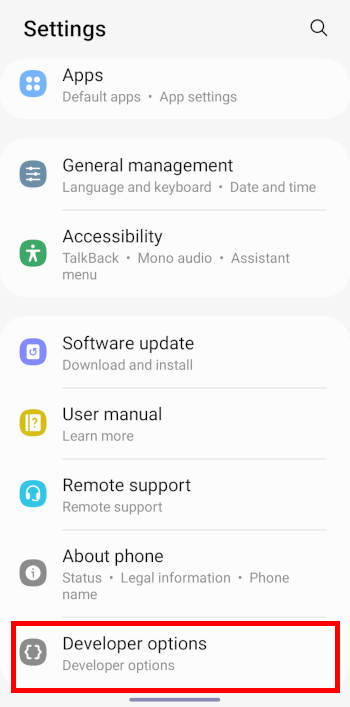
Step 2: Access the software info page
Once on the Galaxy S22 Settings page, scroll down and then tap About phone, as shown in the screenshot below.
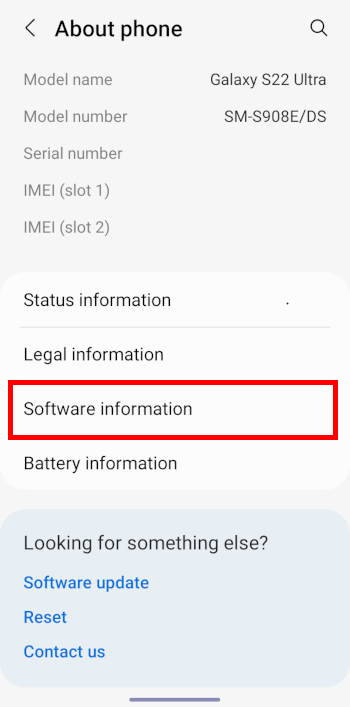
On the About phone page, tap Software information, as shown in the screenshot above.
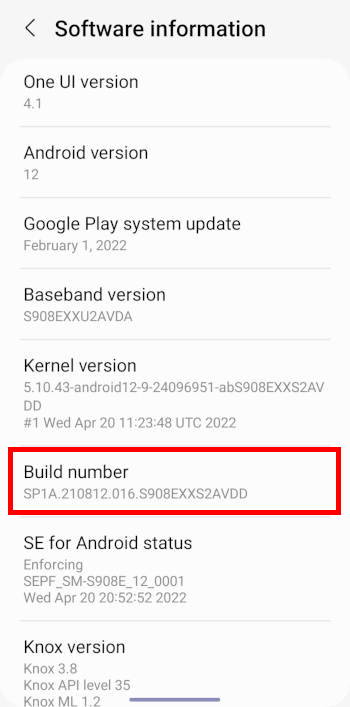
Step 3: Tap Build number 7 times
You can now find the Build number entry on the software information page, as shown in the screenshot below.
Tap Build number 7 times quickly.
Normally, after 3 times, a head-up notification (fade-in then fade-out)will remind you that “you are now x steps away from being a developer”, as shown below.

You just need to continue tapping.
After tapping the Build number 6 times, it will ask you to authenticate yourself with the PIN (or password or pattern, depending on your lock screen security settings).
You will then see the head-up notification telling you that Galaxy S22 developer options are enabled.
Step 4: Access Galaxy S22 developer options
Now, go back to the Galaxy S22 Settings page. You will now notice a new Developer options entry at the bottom, as shown in the screenshot above.
You need to tap Developer options. Then on the Developer options page, enable or disable individual features (read on).
Galaxy S22 developer options explained
Galaxy S22 developer options are organized in the following groups:
- General (1-13).
- Debugging (14-34)
- Networking (35-54).
- Input (55-56).
- Drawing (57-66).
- Hardware-accelerated rendering (67-74).
- Games (75).
- Media (76-77).
- Monitoring (78-79).
- Apps (80-93).
- Autofill (94-97).
- Storage (98).
- Location (99-100).
We now go through all entries in these groups one by one.
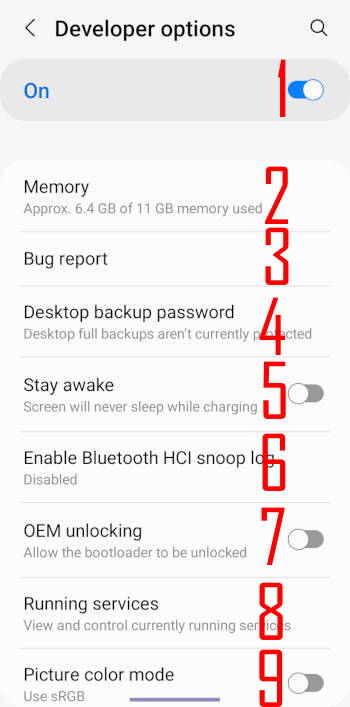
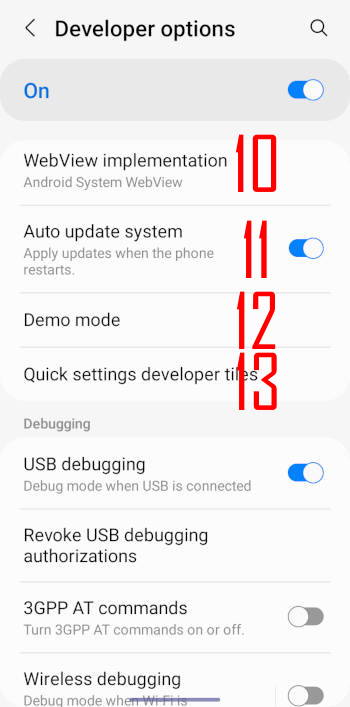
The following 13 entries, as shown in the two screenshots below, can be found in the general group of Galaxy S22 developer options.
1. On/off Galaxy S22 developer options
You can use the switch to turn off Galaxy S22 developer options.
Unlike in previous versions, this is not a “hide” option. If you use this switch to turn off Galaxy S22 developer options, you need to enable it again by tapping the build number 7 times.
2. Memory
You can use it to quickly check the overall memory usage, average usage, and memory usage of processes in the last 3 hours.
So, you can get a bit more information about memory usage than in Device care.
3. Bug report
You can use this option to configure interactive or full bug reports.
4. Desktop backup password
You can set a password to protect the backup to the desktop using the ADB command (adb backup). It is different from your lock screen password/PIN.
This password does NOT affect your backup through other channels. For example, most Galaxy S22 owners back up the phone with the Smart Switch app on the PC. This password is NOT used for such backups.
5. Stay awake
This Galaxy S22 developer option lets you keep the screen always on while charging the battery.
You may also use the Smart Lock to keep the phone unlocked. But the screen still times out.
Normally, you should not turn on this feature. If the screen does not update frequently, the screen may suffer from burn-in damage.
6. Enable Bluetooth HCI snoop log
HCI stands for Host Controller Interface for Bluetooth connections.
You can enable the HCI snoop log to record all Bluetooth transmissions/packets on Galaxy S22.
7. OEM unlocking
By default, you cannot unlock the bootloader on Galaxy S22. Consequently, You cannot install custom recovery or custom ROM and cannot root the phone.
OEM unlocking lets you unlock the bootloader.
In most regions, the standard warranty voids if you unlock the bootloader.
8. Running services
You use running services to check and stop services that are running. It is similar to tasks manager in Windows.
9. Picture colour mode
By default, Galaxy S22 uses the vivid screen mode (under Settings — Display — Screen mode).
However, if you feel the colours are oversaturated and want to use “natural” (or true) colours, you can set the screen mode to Natural.
This Galaxy S22 developer option appears only when the vivid mode is used. You can use it to switch to the natural mode.
10. Webview implementation
By default, it is always the Android system Webview.
11. Auto update system
Galaxy S22 can automatically install some non-critical updates when you restart the system. This applies to updates that are downloaded automatically if you enable Auto download over WiFi in Settings –.Software update.
12. Demo mode
The demo mode is for developers to take clean screenshots by displaying a generic, preset notification bar (system UI). It can only be accessed through the ADB command.
Do not confuse the Demo mode with the Retail mode that Samsung uses in the showroom.
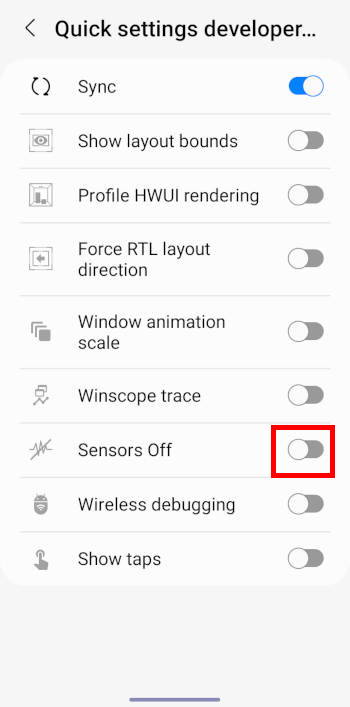
13. Quik settings developer tiles
Developers can use this option to add a few more quick settings buttons.
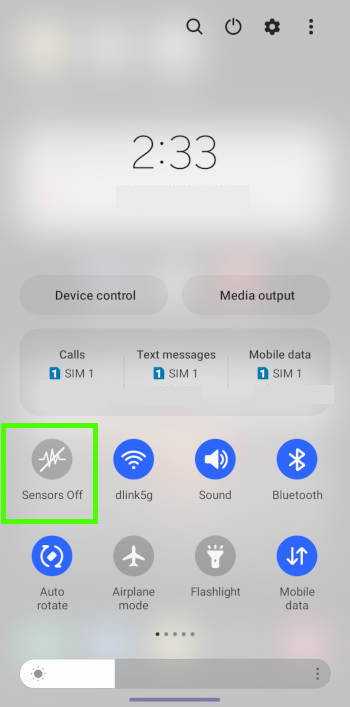
For example, by default, the sensors off button (which turns off all sensors on Galaxy S22) is not available for users. However, you can enable it here, and it will be available in the Galaxy S22 Quick settings panel, as shown in the following two screenshots.
The following 21 entries, as shown in the following 4 screenshots, are under the debugging group of Galaxy S22 developer options. They offer many debugging options for app developers.
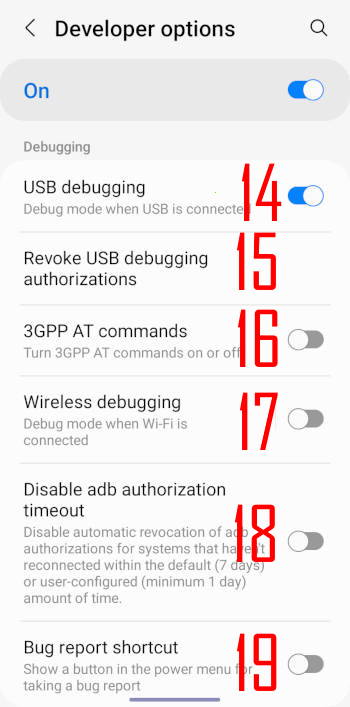
14. USB debugging
USB debugging is one of the most used Galaxy S22 developer options.
Technically, once enabled, Galaxy S22 and the development machine (usually a PC/laptop) can communicate with each other.
If you want to run an ADB command on Galaxy S22 through the USB connection, you must enable USB debugging.
In addition to debugging or side-loading apps, you can also use ADB commands to take screenshots for Galaxy S22 on your PC. You may find this method is more useful than the 5 standard methods of taking screenshots on Galaxy S22 directly when you need to take a lot of screenshots.
15. Revoke USB debugging authorizations
When a development machine is authorized to connect to Galaxy S22, you do not need to re-authorize it again until the authorization times out (read on).
You can revoke USB debugging authorizations manually with this option.
16. 3GPP AT commands
3GPP AT commands are used to control the modem in Galaxy S22.
17. Wireless debugging
Instead of through a USB connection, you can also run the same ADB commands through WIFi connections. This is very common for Android TV sticks, e.g., Chromecast with Android TV.
“Wireless” here actually does not necessarily limit to WiFi. As long as the developer machine and Galaxy S22 are on the same network (and they can “see” each other), you can use wireless debugging. For example, when your PC connects to the Ethernet port of the router and Galaxy S22 connects to the wireless AP, you can also use wireless debugging.
You can even connect Galaxy S22 to an Ethernet port with a USB C to Ethernet adapter to use wireless debugging.
18. Disable adb authorization timeout
By default, the authorization for a developer machine times out if there is no connection in the last 7 days.
You can disable this timeout in the Galaxy S22 developer options so that the authorization never times out.
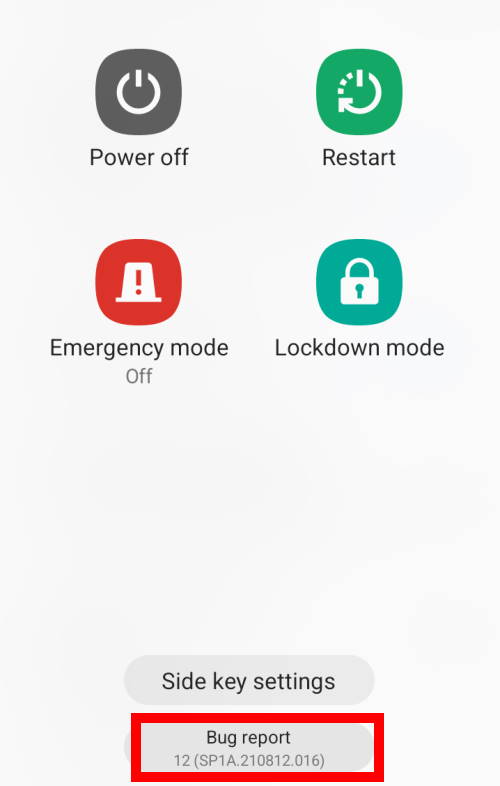
19. Bug report shortcut
If enabled, you will see a bug report button in the Power off menu.
For example, as shown in the screenshot below, you can find the Bug report button at the bottom of the Power-off menu, in addition to the normal Power off, restart, emergency mode, lockdown mode, and Side key settings.
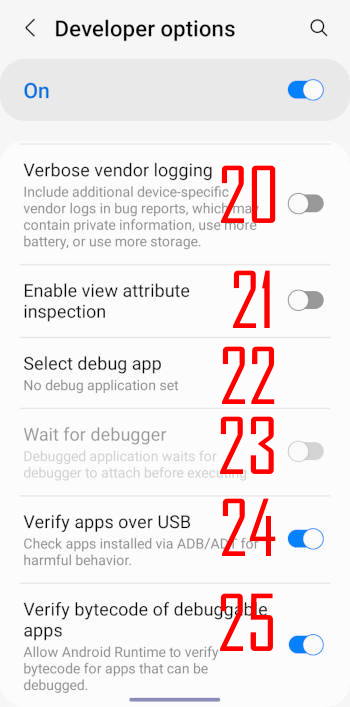
20. Verbose vendor logging
Verbose vendor logging will include additional device-specific vendor logs in bug reports. Some private info may be included in the report. Of course, it will take a longer time to generate the report and use more storage space.
21. Enable view attribute inspection
This option, if enabled, lets you save view attribute information of a View instance so it can be used for debugging. You can access the attribute information through the Layout Inspector.
22. Select debug app
You need to select the app for debugging (through ADB).
23. Wait for debugger
You can choose whether to wait for the debugger before the app (to be debugged) executes.
24. Verify apps over USB
All apps installed through the Play Store, Galaxy Store, or any apps (e.g., sideload an APK through Chrome) are scanned by Google to detect possible harmful behaviour. This process is called “verify”.
Verify apps over USB option, if enabled (the default), will extend the scan to all apps installed through ADB or ADT (Android Development Tools).
25. Verify bytecode of debuggable apps
Bytecode is “compiled” from the source code (e.g., Java) so that Android devices can execute the code more efficiently.
This option lets Android Runtime verify bytecode for apps that can be debugged.
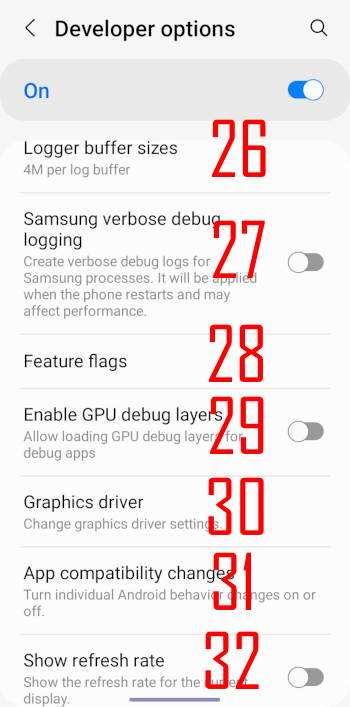
26. Logger buffer sizes
Android logging relies on buffers. Processes and apps write various logs to different buffers. New entries will overwrite old extries.
Logcat reads these entries.
So, if there are too many logs and the buffer size is too small, then some buffers may be overwritten before being read. In other words, you lose some logs.
Larger logger buffer sizes may degrade the system performance if you use the phone heavily.
The default 4M is sufficient for most users.
27. Samsung verbose debug logging
This option creates verbose debug logs for system processes coded by Samsung.
28. Feature flags
Feature flags are mainly for beta features.
Nothing in Galaxy S22.
29. Enable GPU debug layers
Enable GPU debug layers will load Vulkan validation layers from local device storage.
30. Graphics driver
You can specify different graphics drivers (if installed) for individual apps.
31. App compatibility change
This option is for app developers to debug their apps.
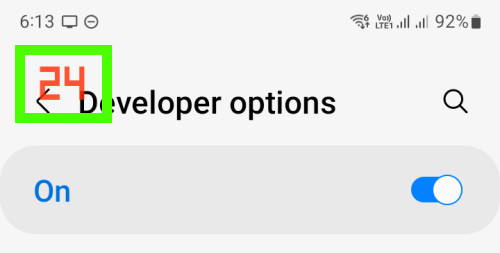
32. Show refresh rate
If enabled, the current refresh rate will be shown near the top left region.
For example, as shown in the screenshot below, the current refresh rate is 24Hz because the motion smoothness was set to adaptive (Settings —Display — Motion smoothness).
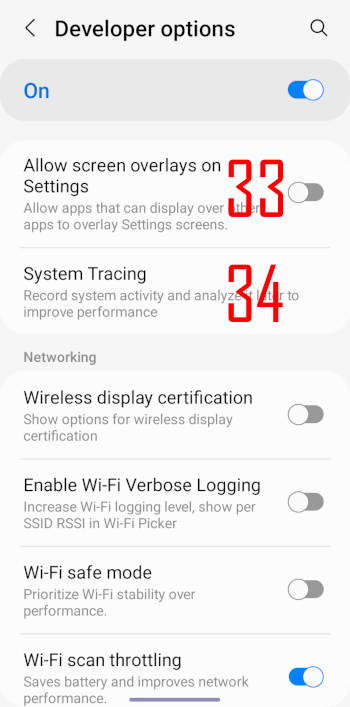
33. Allow screen overlays on Settings
By default, no apps are allowed to overlays Galaxy S22 Settings app.
This option allows you to turn off this restriction.
34. System Tracing
You can use this option to record system activities (trace) so that you can trace back any performance issues. You can see some options after tapping this entry.
A few experienced developers may use system tracing to debug some issues for their apps.
The following 20 entries, as shown in the following 4 screenshots, are networking-related Galaxy S22 developer options. WiFi, mobile data, Bluetooth, and USB connections are all covered.
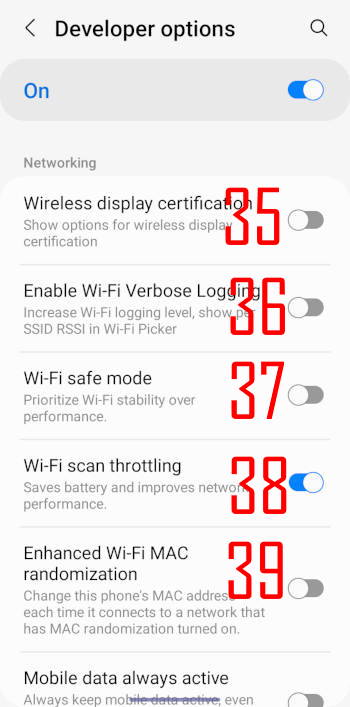
35. Wireless display certification
This option enables advanced configuration controls and settings for Wireless Display certification.
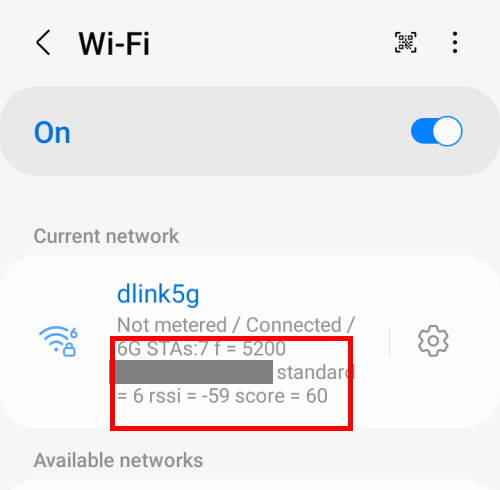
36. Enable Wi-Fi verbose logging
If enabled, this option increases the Wi-Fi logging level and shows per SSID RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) in Wi-Fi picker.
For example, on the WiFi connection page, you can find more details, as shown in the screenshot below.
37. Wi-Fi safe mode
if there are multiple remembered WiFi networks (SSIDs), Galaxy S22 will pick one based on signal strength and performance.
This option changes this behaviour and prioritizes WiFi stability over performance.
38. Wi-Fi scan throttling
Android system and some apps always scan WiFi networks to perform better. But this means more battery drain.
The Wi-Fi scan throttling limits the frequency of such scans.
Normally, you should leave this option on (the default).
39. Enhanced Wi-Fi MAC randomization
Each Galaxy S22 has a unique MAC address for Wi-Fi connections. So, the users may be easily tracked.
Since Android 10, Android uses randomized MAC addresses by default. You can enable or disable it for each network connection.
By default, the randomized MAC address for an individual access point is persistent. In other words, for one router, Galaxy S22 uses one randomized MAC address until you do a factory data reset on the phone (or the router).
The enhanced Wi-Fi MAC randomization makes the address non-persistent. The MAC address changes for each new connection.
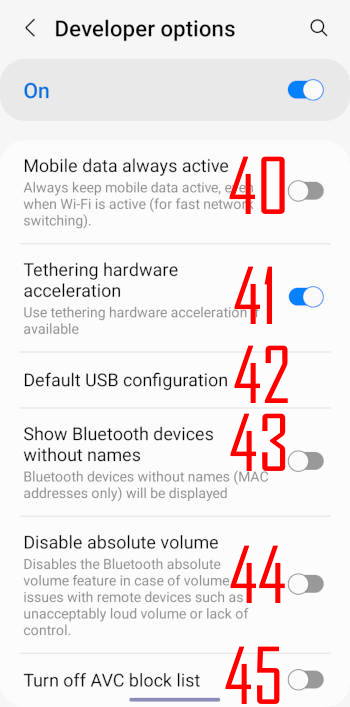
40. Mobile data always active
By default, when Wi-Fi is connected, the mobile data connection is automatically suspended to save battery.
Once the Wi-Fi network is not available, a mobile data connection will be established automatically.
Mobile data always active options lets you keep mobile data active even when Wi-Fi is connected. In this case, the Wi-Fi connection is actually used. Mobile data is active so that the switch from Wi-Fi to mobile data will be faster. Of course, it will drain more battery.
41. Tethering hardware acceleration
Use tethering hardware acceleration if available. So, it can improve battery life when handing off tethering functionality to separate hardware.
42. Default USB configuration
You can choose the default USB configuration to:
- Transferring files.
- USB tethering.
- MIDI.
- Transferring images.
- Charging Galaxy S22 battery only.
You can change the configuration in the notification panel once the USB connection is established.
43. Show Bluetooth devices without names
You can choose to show all Bluetooth devices nearby, including those without names (with MAC address only).
44. Disable absolute volume
By default, when you adjust the volume in your Bluetooth headphones, you will see the volume slider changes on Galaxy S22 as well. Similarly, in the Galaxy volume slider, you can find one for your Bluetooth headset (when connected). This is what “absolute” volume means: the volume control is synced in the headset and Galaxy S22.
However, If your Bluetooth headset volume is too low or too high, you might try to disable absolute volume.
45. Turn off AVC block list
Some app developers may use non-compliant codecs in their apps for some reason. These codecs are categorised as Advanced Video Coding (AVC).
By default, Galaxy S22 uses AVC block list. You may turn on this option if a few app developers ask you to turn on it for their apps.
46. Turn off A2DP hardware offload
You should NOT turn on this option unless you get some audio quality or connection issues.
Hardware offloading A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile) should normally improve the audio quality and connection. By default, almost all Android phones enable A2DP hardware offload.
47. Bluetooth AVRCP version
You can choose the Bluetooth AVRCP (Audio/Video Remote Control Profile) version from 1.3 up to 1.6. The default version on Galaxy S22 is 1.5.
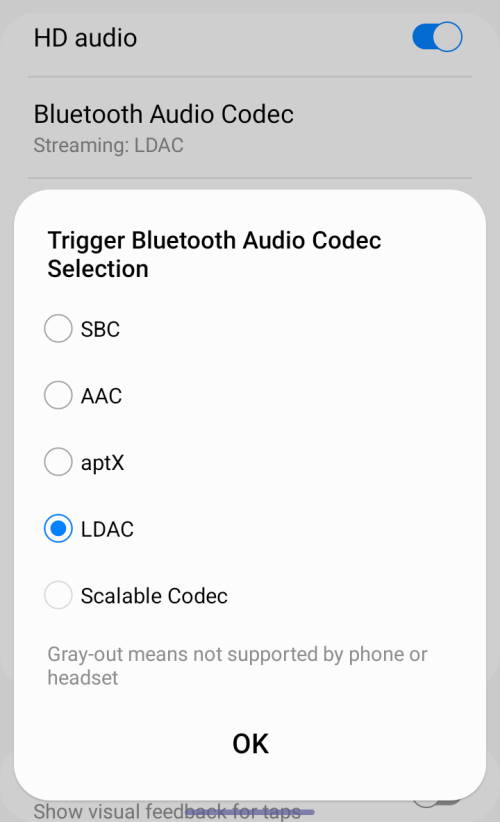
48. HD audio
This option is available only when a Bluetooth headset supports AptX or LDAC or Scalable Codec is connected.
For example, as shown in the screenshot below, I can turn on or off HD audio after a supported headphone is connected. I can also change the codec, sample rate, and audio bits.
Scalable codecs are supported by all Samsung’s earbuds (Galaxy Buds, Galaxy Buds+, Galaxy Buds Live, Galaxy Buds Pro, and Galaxy Buds 2). The new Samsung Seamless Codec supported by Galaxy Buds Pro 2 (and Galaxy S22) is just a new version of Scalable Codec. In some regions, it will not be listed as a new codec.
LDAC codec is supported by some Sony headphones (e.g., WH-1000XM series) and earbuds (e.g., WF-1000XM4/XM5).
49. Bluetooth audio codec
You can only choose Bluetooth audio codec after the headset is connected to Galaxy S22.
By default, Galaxy S22 will try the HD codecs (aptX, LDAC or Scalable).
Once the headset is connected to Galaxy S22, you can actually change the codec in the Bluetooth settings for some connected devices.
50. Bluetooth Audio sample rate
This option depends on the active audio codec. So, you can only change it after a headset is connected to Galaxy S22.
51. Bluetooth audio bits per sample
You can only change it after a headset is connected to Galaxy S22.
52. Bluetooth audio channel mode
You can only change this option after a headset is connected to Galaxy S22.
By default, the most connected headsets are stereo.
53. Bluetooth audio LDAC codec
You can only change this option after a supported headset is connected to Galaxy S22.
Please refer to this guide on how to enable Hi-Res Audio with LDAC codec on Galaxy S22 and S23.
54. Bluetooth PBAP
You can choose the Phone Book Access Profile (PBAP) 1.2 or 1.1.
The following 2 entries are under the input group of Galaxy S22 developer options. They are shown in the screenshot earlier (marked as 55 and 56).
55. Show taps
This option lets you show visual feedback for taps.
56. Pointer location
This option overlay information on the current touch location.
Below the status bar, an information bar tracking the touch location coordinates will appear.
Of course, these two options are purely for app debugging, not for normal use.
The following 10 entries, as shown in the following 2 screenshots, are under the Drawing group of Galaxy S22 developer options. They change how the contents are displayed, mainly animated, on the screen.
57. Show surface updates
This option, once enabled, will flash entire window surfaces when they update.
58. Show layout bounds
You can use this option to show the current app’s clip bounds, margins, and other user interface constructions on the screen.
59. Force RTL layout direction
You can force the screen layout direction to be from right to left (RTL) for all locales.
The default layout direction on Galaxy S22 depends on your locale (language). In most regions, it is from left to right (LTR). This option will force the RTL layout regardless of the locale settings.
60. Windo animation scale
You can set a “multiplier” for the window animation playback speed.
A lower scale will result in a faster speed of window animation. So, the new window will pop up (and fade) faster. This does not actually make Galaxy S20 slower or faster. But It does let you “feel” it is faster when you lower the Window animation scale.
If you turn off the animation, the speed will be limited by the hardware (and software) only.
61. Transition animation scale
The option is for the speed scale for transition animations.
62. Animation duration scale
You can set a multiplier for the animation duration.
A lower animation duration scale results in shorter (and therefore faster) animation.
If you want to make the phone looks as fast as possible, you can try to turn off animations.
Please note, it is safe to turn off all these animations to make the phone actually faster.
63. Simulate secondary displays
You can add a secondary display from 480p to 4K as an overlay on the current screen so that you can check the layout on screens with different sizes.
Of course, this option is mainly for app developers.
64. Minimum width
You probably should not change the minimum width.
65. Simulate display cutout
Galaxy S22 screen has a punch-hole cutout for the front camera.
So, you should use the default one. Other options (corner cutout, double cutout, tall cutout and waterfall cutout) are for app developers to test their apps.
Using improper display cutout may freeze the phone.
66. Show Text ID
It is probably for app developers to debug the UI.
The following 8 entries are under the Hardware accelerated rendering group of Galaxy S22 developer options. Hardware-accelerated rendering means the graphics are processed by GPU. Four of the entries (67-70) are shown in the screenshot above. The other four (71-74) are shown in the screenshot below.
67. Show view updates
This option lets you flash views inside windows when drawn.
68. Show hardware layer update
Once enabled, the screen flashes hardware layers green when they update.
69. Debug GPU overdraw
This option allows developers to check how many times the same pixel has been drawn in the same frame.
70. Debug non-rectangular clip operations
You can use this option to disable the clipping area on the canvas to create unusual (non-rectangular) canvas areas.
71. Force dark mode
Many apps still do not support the dark mode. This developer option lets you force all apps to use the dark mode even if not supported,
72. Force 4x MSAA
This option enables multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) in Open GL ES 2.0 apps.
73. Disable HW overlays
Hardware overlay enables each app that displays something on the screen to use less processing power.
If you turn on this option (i.e., disable HW overlays), an app shares the video memory and has to constantly check for collision and clipping to render a proper image. The checking uses a lot of processing power.
74. Simulate colour space
You can use this option to change the colour scheme of the entire system UI to cater for various types of colour blindness..
You can choose from:
- Disabled (the default).
- Monochromacy (black, white, and grey).
- Deuteranomaly (red-green).
- Protanomaly (red-green).
- Tritanomaly (blue-yellow).
The following 5 entries, as shown in the screenshot below, are under the Games (75), Media (76-77), and Monitoring (78-79) groups of Galaxy S22 developer options.
75. GPUWatch
You can enable it to get information about an app’s CPU/GPU usage, frame rate and GPU activities as a floating widget.
76. Disable USB audio routing
This option lets you disable automatic routing to external audio peripherals connected to the USB port of the Galaxy S22.
As there is no standard for “USB audio”, many external USB DACs require USB audio routing.
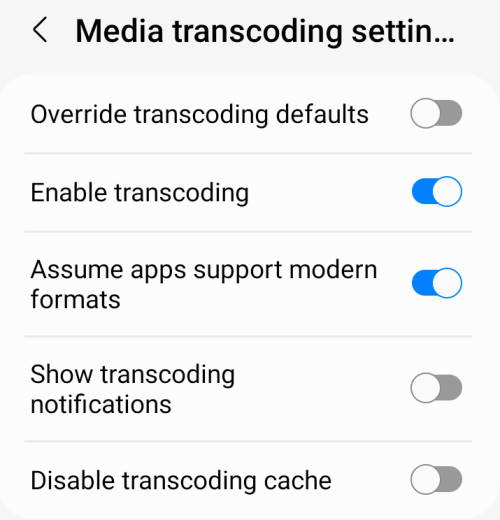
77. Media transcoding settings
Transcoding is essential for modern media files. The media transcoding settings in the Galaxy S22 developer options lets you alter (you probably should not) the default settings, as shown in the screenshot below.
Please do not disable “enable transcoding”.
78. Strict mode enabled
You can flash the screen when apps do long operations on the main thread.
79. Profile HWUI rendering
This option lets you display the GPU rendering profile. You can choose to display the info on the screen as bars or in the ADB shell dumpsys gfxinfo.
The following 14 entries, as shown in the following 3 screenshots, are in the Apps group of Galaxy S22 developer options. These are frequently used features of Galaxy S22 developer options.
80. Don’t keep activities
You can destroy every activity as soon as the user leaves the activity’s main view.
It may save some battery. But sometimes, it may just use more battery.
81. Background process limit
This option is for you to set the number of processes that can run in the background at one time.
You can change it from the standard limit (default) to 0-4 processes.
82. Background check
The background check option lets you check which apps are allowed to have background activities.
83. Always show crash dialog
If enabled, a pop-up dialogue appears every time an app crashes.
84. Show background ANRs
You can use this option to show Apps Not Responding dialogue for background apps. It is usually not necessary for most Galaxy S22 owners.
85. Suspend execution for cached apps
As Galaxy S22 and many other flagship Android phones have more than enough memory (RAM), some apps are cached in the memory.
For example, if you close the Chrome app and open your Gmail app. Chrome app is very likely cached in the memory, instead of being closed (cleaned from the memory). So, when you want to switch to Chrome, it will be loaded instantly.
By default, cached apps in Android are not frozen. They are actually still active. They may still use CPU and other resources in the background.
Suspend execution for cached apps option does what it claims: freeze the app. The impacts are:
- Save some battery (good for battery).
- Slow to switch/update (bad for multitasking)
You need to reboot Galaxy S22 if you make any changes to this option.
Please check this guide on how to use Suspend execution for cached apps on Galaxy S22.
86. Show notification channel warnings and reset notification importance
Displays on-screen warning when an app posts a notification without a valid channel.
87. Standby apps
Android 12 uses the App Standby Buckets to help the system prioritize apps’ requests for resources based on how recently and how frequently the apps are used. These are done automatically.
The standby apps option lets you manually assign an app into one of the following 5 groups:
- Active: App is currently being used or was very recently used.
- Working set: App is in regular use.
- Frequent: App is often used, but not every day.
- Rare: App is not frequently used.
- Restricted: App consumes a great deal of system resources, or may exhibit undesirable behavior.
Resource restrictions for each group are different.
Some apps may be greyed out because you did not use them for a long time. For these apps, you can open them, and then change the group from Active to the one you want to use.
88. Force allow apps on external
You can make any apps eligible to be written to external storage, regardless of the manifest values.
This option is not relevant to Galaxy S22.
89. Force activities to be resizable
If enabled, you can make all activities resizable for multiwindow, regardless of the manifest values.
90. Enable freeform windows
You can enable the freedom windows for all apps (you need to enable force activities to be resizable as well).
Freeform windows are similar, but not identical to the pop-up view.
91. Force desktop mode
This option is not needed for Galaxy S22.
You can always use Samsung DeX (or DeX for PC) when connecting the phone to an external display.
The desktop mode here refers to Android 12’s desktop mode, which is still experimental.
92. Multi-window for all apps
This option allows non-resizable apps to appear in multiwindow (when selecting apps for the second app in the split-screen view).
In the Android 13 (One UI 5) update for Galaxy S22, S21, and S20, you can enable this option in Settings — Advanced features –Labs.
Please refer to this guide on how to use multiwindow on Galaxy S22.
93. Reset the ShortcutManager API call limit
This option is for developers to test apps.
Reset the limit allows the background apps can continue to call shortcut APIs until the rate limit is reached again.
The following 7 entries, as shown in the screenshot below, are in the Autofill, Storage, and Location groups of Galaxy S22 developer options.
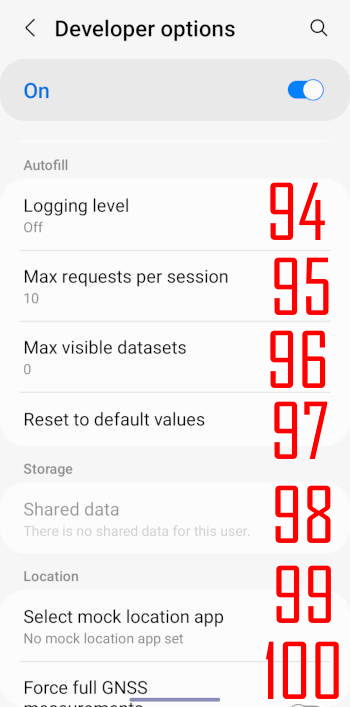
94. Logging level
You can choose the logging level or autofill to none, verbose, or debug.
95. Max requests per session
This option sets the maximum requests for the autofill service in one session. The default is 10.
96. Max visible datasets
The default value for the max visible datasets is 0.
97. Reset to default values
It resets the above 3 entries to the default.
98. Shared data
This option is not relevant to Galaxy S22.
99. Select mock location app
You can spoof the GPS location of the Galaxy S22.
You need to download a GPS spoofing app to manually set your location. This does not affect the location services on Galaxy S22.
100. Force full GNSS
Track all GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) constellations and frequencies with no duty cycling.
Do you have any questions on Galaxy S22 developer options?
If you have any questions about Galaxy S22 developer options on Galaxy S22, S22+, and S22 Ultra, please let us know in the comment box below.
The community will help you.
You may check other Galaxy S22 guides:
- Galaxy S22 new features guides, including Android 13 (One UI 5.0 and One UI 5.1) update and Android 14 (One UI 6) update.
- Galaxy S22 how-to guides.
- Galaxy S22 camera guides.
- Galaxy S22 accessories guide.
- Official Galaxy S22 user manuals (in PDF).
If you want to discuss any issues privately, you can reach us through:
- Facebook page.
- WhatsApp (coming soon).
- Contact form.
Please do not forget to subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest updates, guides, tips, and tricks for Galaxy S22, S22+, and S22 Ultra.








Leigh E Johnson says
Easy to understand and very helpful guide. Thank you much!